Elastic.Transport
0.11.1
Prefix Reserved
dotnet add package Elastic.Transport --version 0.11.1
NuGet\Install-Package Elastic.Transport -Version 0.11.1
<PackageReference Include="Elastic.Transport" Version="0.11.1" />
<PackageVersion Include="Elastic.Transport" Version="0.11.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Elastic.Transport" />
paket add Elastic.Transport --version 0.11.1
#r "nuget: Elastic.Transport, 0.11.1"
#:package Elastic.Transport@0.11.1
#addin nuget:?package=Elastic.Transport&version=0.11.1
#tool nuget:?package=Elastic.Transport&version=0.11.1
Elastic.Transport
Transport classes and utilities shared among .NET Elastic client libraries. Provides cluster-aware, resilient HTTP transport optimized for the Elastic product suite and Elastic Cloud.
Installation
dotnet add package Elastic.Transport
Quick Start
var settings = new TransportConfiguration(new Uri("http://localhost:9200"));
var transport = new DistributedTransport(settings);
// GET request — returns body as string
var response = transport.Get<StringResponse>("/my-index/_search?q=title:hello");
// POST request — send JSON body
var body = PostData.String(@"{ ""query"": { ""match_all"": {} } }");
var searchResponse = transport.Post<StringResponse>("/my-index/_search", body);
// HEAD request — no body needed
var headResponse = transport.Head("/my-index");
// JSON DOM with safe path traversal
var jsonResponse = transport.Get<JsonResponse>("/my-index/_search?q=title:hello");
int totalHits = jsonResponse.Get<int>("hits.total.value");
string firstId = jsonResponse.Get<string>("hits.hits.[0]._id");
// Async variants
var asyncResponse = await transport.GetAsync<StringResponse>("/my-index/_search?q=title:hello");
Response Types
The generic type parameter on Get<TResponse>, Post<TResponse>, etc. controls how the response body is read:
| Type | Body Representation | Notes |
|---|---|---|
StringResponse |
string |
Good for debugging and small payloads |
BytesResponse |
byte[] |
Raw bytes, useful for binary content |
VoidResponse |
(skipped) | Body is not read. Used for HEAD and fire-and-forget calls |
StreamResponse |
Stream |
Caller must dispose. Best for large payloads |
JsonResponse |
JsonNode |
System.Text.Json DOM with safe Get<T>() path traversal |
DynamicResponse |
DynamicDictionary |
Legacy — prefer JsonResponse |
JsonResponse
JsonResponse deserializes JSON into a System.Text.Json.Nodes.JsonNode and exposes a Get<T>() method for safe, typed path traversal using dot-separated keys:
var response = transport.Get<JsonResponse>("/my-index/_search?q=title:hello");
// Traverse nested JSON with dot notation
int totalHits = response.Get<int>("hits.total.value");
string firstId = response.Get<string>("hits.hits.[0]._id");
// Bracket syntax for array access
string lastId = response.Get<string>("hits.hits.[last()]._id");
string firstSource = response.Get<string>("hits.hits.[first()]._source.title");
// _arbitrary_key_ traverses into the first key at that level
string fieldType = response.Get<string>("my-index.mappings.properties._arbitrary_key_.type");
// Direct DOM access is also available via .Body
JsonNode hitsNode = response.Body["hits"]["hits"];
Configuration
Single node
var settings = new TransportConfiguration(new Uri("http://localhost:9200"));
Elastic Cloud (cloud ID)
var settings = new TransportConfiguration("my-cloud-id", new ApiKey("base64key"));
// or
var settings = new TransportConfiguration("my-cloud-id", new BasicAuthentication("user", "pass"));
Multiple nodes with a node pool
var pool = new StaticNodePool(new[]
{
new Node(new Uri("http://node1:9200")),
new Node(new Uri("http://node2:9200")),
new Node(new Uri("http://node3:9200"))
});
var settings = new TransportConfiguration(pool);
var transport = new DistributedTransport(settings);
All components
var pool = new StaticNodePool(new[] { new Node(new Uri("http://localhost:9200")) });
var requestInvoker = new HttpRequestInvoker();
var product = ElasticsearchProductRegistration.Default;
var settings = new TransportConfiguration(pool, requestInvoker, productRegistration: product);
var transport = new DistributedTransport(settings);
Request Pipeline
The transport models a request pipeline that handles node failover, sniffing, and pinging:
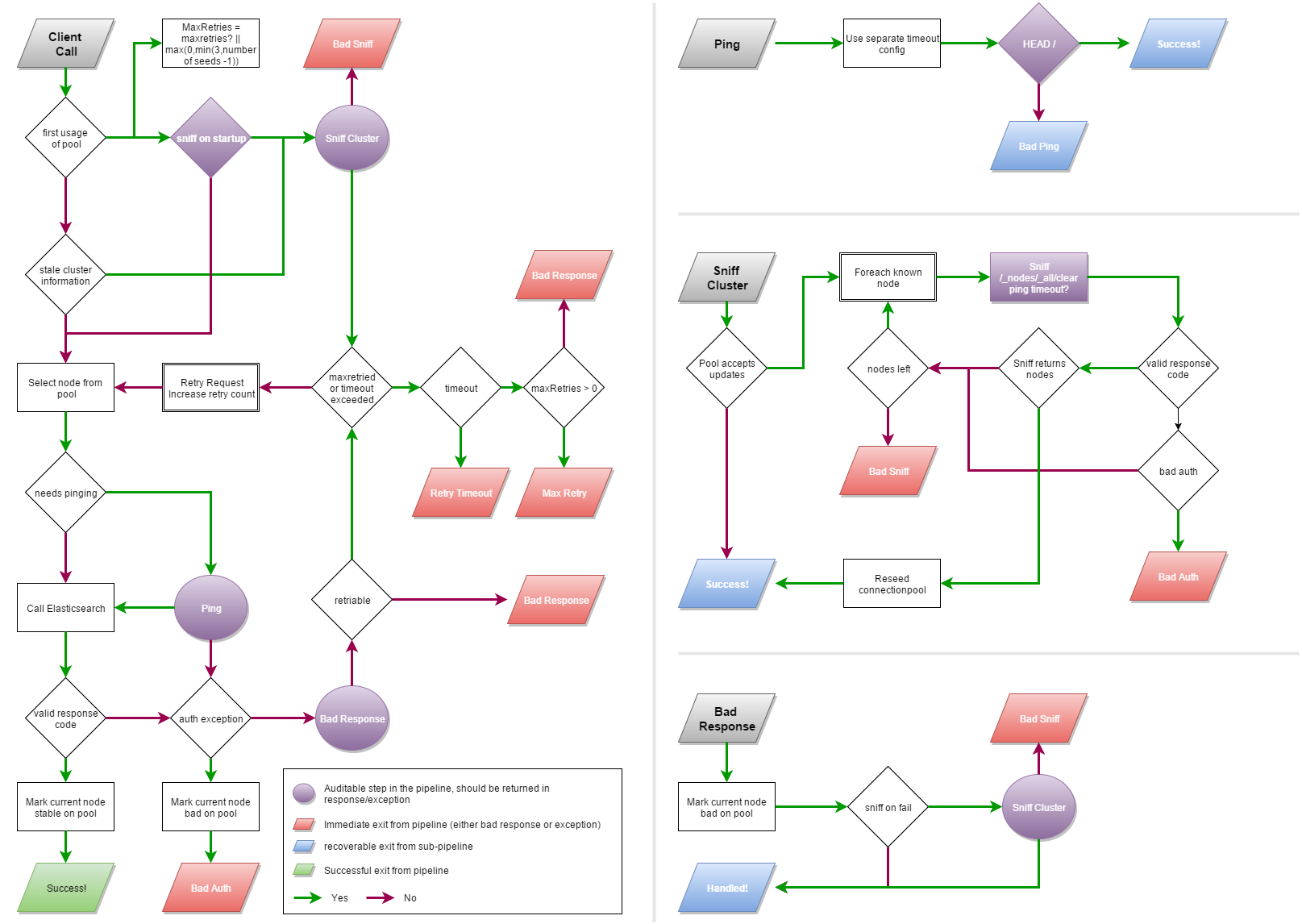
The pipeline introduces two special API calls:
- Sniff — queries the cluster to discover the current node topology
- Ping — the fastest possible request to check if a node is alive
The transport fails over in constant time. If a node is marked dead, it is skipped immediately (as long as the overall request timeout allows).
Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
NodePool |
Registry of Node instances. Implementations: SingleNodePool, StaticNodePool, SniffingNodePool, StickyNodePool, CloudNodePool |
IRequestInvoker |
Abstraction for HTTP I/O. Default: HttpRequestInvoker |
Serializer |
Request/response serialization. Default uses System.Text.Json |
ProductRegistration |
Product-specific metadata, sniff/ping behavior. Use ElasticsearchProductRegistration for Elasticsearch |
Observability
Every response inherits from TransportResponse and exposes an ApiCallDetails property:
var response = transport.Get<StringResponse>("/");
// Structured call metadata
ApiCallDetails details = response.ApiCallDetails;
Console.WriteLine(details.HttpStatusCode);
Console.WriteLine(details.Uri);
// Human-readable debug string
Console.WriteLine(details.DebugInformation);
The transport also emits DiagnosticSource events for serialization timing, time-to-first-byte, and other counters.
Custom Typed Responses
Any class inheriting from TransportResponse can be used as a response type. The transport will deserialize the response body into it using System.Text.Json:
public class SearchResult : TransportResponse
{
[JsonPropertyName("hits")]
public HitsContainer Hits { get; set; }
}
public class HitsContainer
{
[JsonPropertyName("total")]
public TotalHits Total { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("hits")]
public List<Hit> Hits { get; set; }
}
public class TotalHits
{
[JsonPropertyName("value")]
public long Value { get; set; }
}
public class Hit
{
[JsonPropertyName("_id")]
public string Id { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("_source")]
public JsonNode Source { get; set; }
}
// Use it directly as a type parameter
var response = transport.Get<SearchResult>("/my-index/_search?q=title:hello");
long total = response.Hits.Total.Value;
For full control over how a response is built from the stream, implement TypedResponseBuilder<TResponse> and register it via ResponseBuilders on the configuration:
public class CsvResponse : TransportResponse
{
public List<string[]> Rows { get; set; }
}
public class CsvResponseBuilder : TypedResponseBuilder<CsvResponse>
{
protected override CsvResponse Build(ApiCallDetails apiCallDetails, BoundConfiguration boundConfiguration,
Stream responseStream, string contentType, long contentLength)
{
using var reader = new StreamReader(responseStream);
var rows = new List<string[]>();
while (reader.ReadLine() is { } line)
rows.Add(line.Split(','));
return new CsvResponse { Rows = rows };
}
protected override async Task<CsvResponse> BuildAsync(ApiCallDetails apiCallDetails, BoundConfiguration boundConfiguration,
Stream responseStream, string contentType, long contentLength, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
using var reader = new StreamReader(responseStream);
var rows = new List<string[]>();
while (await reader.ReadLineAsync(cancellationToken) is { } line)
rows.Add(line.Split(','));
return new CsvResponse { Rows = rows };
}
}
var settings = new TransportConfiguration(new Uri("http://localhost:9200"))
{
ResponseBuilders = [new CsvResponseBuilder()]
};
AOT and Source Generators
The default serializer uses System.Text.Json with a JsonSerializerContext for AOT compatibility. When using custom typed responses in AOT/trimmed applications, provide a JsonSerializerContext that includes your response types:
[JsonSerializable(typeof(SearchResult))]
[JsonSerializable(typeof(HitsContainer))]
[JsonSerializable(typeof(TotalHits))]
[JsonSerializable(typeof(Hit))]
public partial class MySerializerContext : JsonSerializerContext;
Create a concrete serializer that combines your context with the transport's built-in resolvers:
public class MySerializer : SystemTextJsonSerializer
{
public MySerializer() : base(new TransportSerializerOptionsProvider([], null, options =>
{
options.TypeInfoResolver = JsonTypeInfoResolver.Combine(
MySerializerContext.Default,
new DefaultJsonTypeInfoResolver()
);
})) { }
}
var settings = new TransportConfiguration(
new SingleNodePool(new Uri("http://localhost:9200")),
serializer: new MySerializer()
);
Links
| Product | Versions Compatible and additional computed target framework versions. |
|---|---|
| .NET | net5.0 was computed. net5.0-windows was computed. net6.0 was computed. net6.0-android was computed. net6.0-ios was computed. net6.0-maccatalyst was computed. net6.0-macos was computed. net6.0-tvos was computed. net6.0-windows was computed. net7.0 was computed. net7.0-android was computed. net7.0-ios was computed. net7.0-maccatalyst was computed. net7.0-macos was computed. net7.0-tvos was computed. net7.0-windows was computed. net8.0 is compatible. net8.0-android was computed. net8.0-browser was computed. net8.0-ios was computed. net8.0-maccatalyst was computed. net8.0-macos was computed. net8.0-tvos was computed. net8.0-windows was computed. net9.0 was computed. net9.0-android was computed. net9.0-browser was computed. net9.0-ios was computed. net9.0-maccatalyst was computed. net9.0-macos was computed. net9.0-tvos was computed. net9.0-windows was computed. net10.0 is compatible. net10.0-android was computed. net10.0-browser was computed. net10.0-ios was computed. net10.0-maccatalyst was computed. net10.0-macos was computed. net10.0-tvos was computed. net10.0-windows was computed. |
| .NET Core | netcoreapp2.0 was computed. netcoreapp2.1 was computed. netcoreapp2.2 was computed. netcoreapp3.0 was computed. netcoreapp3.1 was computed. |
| .NET Standard | netstandard2.0 is compatible. netstandard2.1 is compatible. |
| .NET Framework | net461 was computed. net462 is compatible. net463 was computed. net47 was computed. net471 was computed. net472 was computed. net48 was computed. net481 was computed. |
| MonoAndroid | monoandroid was computed. |
| MonoMac | monomac was computed. |
| MonoTouch | monotouch was computed. |
| Tizen | tizen40 was computed. tizen60 was computed. |
| Xamarin.iOS | xamarinios was computed. |
| Xamarin.Mac | xamarinmac was computed. |
| Xamarin.TVOS | xamarintvos was computed. |
| Xamarin.WatchOS | xamarinwatchos was computed. |
-
.NETFramework 4.6.2
- Microsoft.CSharp (>= 4.7.0)
- System.Diagnostics.DiagnosticSource (>= 10.0.0)
- System.Text.Json (>= 10.0.0)
-
.NETStandard 2.0
- Microsoft.CSharp (>= 4.7.0)
- System.Diagnostics.DiagnosticSource (>= 10.0.0)
- System.Text.Json (>= 10.0.0)
-
.NETStandard 2.1
- Microsoft.CSharp (>= 4.7.0)
- System.Diagnostics.DiagnosticSource (>= 10.0.0)
- System.Text.Json (>= 10.0.0)
-
net10.0
- No dependencies.
-
net8.0
- System.Diagnostics.DiagnosticSource (>= 10.0.0)
- System.Text.Json (>= 10.0.0)
NuGet packages (7)
Showing the top 5 NuGet packages that depend on Elastic.Transport:
| Package | Downloads |
|---|---|
|
Elastic.Clients.Elasticsearch
This strongly-typed, client library enables working with Elasticsearch. It is the official client maintained and supported by Elastic. |
|
|
Elastic.Ingest.Transport
Provides components to build a buffer-backed channel for publishing events to distributed systems over HTTP through Elastic.Transport |
|
|
Elastic.Transport.VirtualizedCluster
Provides a way to assert transport behaviour through a rule engine backed VirtualClusterConnection |
|
|
Elastic.Ingest
Provides components to build a buffer-backed channel for indexing documents into Elasticsearch |
|
|
Dnet.Elastic.Clients.Elasticsearch
This strongly-typed, client library enables working with Elasticsearch. It is the official client maintained and supported by Elastic. |
GitHub repositories (1)
Showing the top 1 popular GitHub repositories that depend on Elastic.Transport:
| Repository | Stars |
|---|---|
|
elastic/elasticsearch-net
This strongly-typed, client library enables working with Elasticsearch. It is the official client maintained and supported by Elastic.
|
| Version | Downloads | Last Updated |
|---|---|---|
| 0.11.1 | 109 | 2/17/2026 |
| 0.11.0 | 304 | 2/16/2026 |
| 0.10.3 | 125,451 | 1/22/2026 |
| 0.10.2 | 7,038 | 12/8/2025 |
| 0.10.1 | 1,451,186 | 8/19/2025 |
| 0.10.0 | 971,660 | 8/12/2025 |
| 0.9.2 | 872,899 | 5/29/2025 |
| 0.9.1 | 1,191 | 5/28/2025 |
| 0.9.0 | 1,027 | 5/28/2025 |
| 0.8.1 | 3,678 | 5/26/2025 |
| 0.8.0 | 357,666 | 5/20/2025 |
| 0.7.0 | 1,552 | 5/19/2025 |
| 0.6.1 | 2,485 | 5/16/2025 |
| 0.5.9 | 1,886,800 | 3/16/2025 |
| 0.5.8 | 73,424 | 2/3/2025 |
| 0.5.7 | 1,901,462 | 12/19/2024 |
| 0.5.6 | 2,621,246 | 11/25/2024 |
| 0.5.5 | 51,208 | 11/21/2024 |
| 0.5.4 | 1,117 | 11/21/2024 |